AREA BACKGROUND
GEOGRAPHICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Palawan is situated in the west of the Philippines chain of islands. It reclines between Mindoro Island and North Borneo. It is bounded on the east by the Sulu Sea and on the west of the Philippines chain of islands. It reclines between Mindoro Island and North Borneo. It is bounded on the east by the Sulu Sea and on the west by the South China Sea. The southern tip of the province is only 97 kms. away from Sabah.
The province is isolated from the rest of the country. However, it occupies a strategic location in terms of national security, tourism and trade. As part of the southern backdoor, it can serve as a convenient part of entry for goods and tourists from other Southeast Asian countries. In fact, its domestic airport was now converted into an international airport. Balabac, its southernmost island municipality, is only 60 miles from Sabah or North Borneo, Malaysia.
At present, the province is composed of twenty three (23) municipalities and one city. The smallest municipality is that of Kalayaan created by virtue of PD 1569 dated June 11, 1978. Puerto Princesa City is the capital of Palawan and serves as the chief seaport of the province.
The main island of Palawan is divided into east and west coasts by chain of tall mountains which centrally runs its entire length. Being mainly forest, it is a haven of different kinds of animal species. The mountain ranges average 1,968 meters high with its highest peak, Mt. Montalingahan in the south at 2,074 meters. Except for the wide plain in the north and pockets of big valleys and delta land along the shore down to the south, the west coast is practically devoid of coastal land and consists mainly of craggy foothills and mountains close to the sea. Rivers and streams abound throughout the province, but the most unusual which is now a major tourist attraction, is the seven-kilometer underground river flowing under limestone rocks and emptying into St. Paul Bay.
Palawan, the largest province in the country today, has a total land area of 14,896.3 square kilometers (1,489,629 has) representing 4.96 percent of the total land area of Philippine territory. It is composed of 1,768 islands and islets, and is 650 kms. long with a total coastline of 1,959 kilometers. The biggest island is the mainland of Palawan which is 425 kilometers long, 40 kilometers at its widest at Brooke’s Point and 8.5 kilometers at its narrowest at Bahile, Puerto Princesa City.
Palawan has two types of climate. The first type which occurs in the northern and southern extremities and the entire western coast has two distinct seasons- six months dry and six months wet. The other type, which prevails in the east coast, has a short dry season of one to three months and no pronounced rainy period during the rest of the year. The southern part of the province is practically free from typhoons but the northern part has persistent gales and torrential rain during July and August. From April to June, however, the weather is calm on both eastern and western sides of Palawan. It is during these months that sea travel is most favorable.
SOCIO-ECONOMIC PROFILE AND OUTLOOK
As of May 2000, Palawan has a total population of 755,412. Its total number of families is 144,874 and the family yearly average of expenditures is P87,035.00. Its annual geometric growth rate is 4.38 percent. Much of the recent rise of the population size is attributable to Puerto Princesa City averaging a yearly growth rate of 5.67 percent. Despite Puerto Princesa’s sharp growth rate, the increase of the provincial population density for the province during the past twenty years was only modest, from 25 persons per square kilometer, to 44 persons per square kilometer, the most sparsely populated among the 73 provinces.
Palawan’s economy is basically agricultural, with fishing and mining playing secondary roles. Agriculture, which is 82.11 % of Palaweños main source of income, consists mainly of raising two main products- rice and coconut. Other agricultural products grown are bananas, root crops as camote and cassava, corn, cashew, and vegetables. Poultry and livestock are still inadequate to supply the meat requirement of the populace.
The province contributes 66 % to the total fish production of the country. Fishing is a year-round activity with the biggest catch from January to October.
Known for its rich deposits of minerals, metallic and non-metallic, it has the biggest reserve of Mercury in the Far East. Further, it has 14 colors of marble of which its black marble is comparable to the Italian finest black marble. Palawan is also rich in nickel, copper, manganese, chromites and has a huge deposit of natural gas.
Palawan is also a haven of beautiful tourist spots being the Philippines’ last frontier. Foreigners from different places regularly visits the attractive places of Palawan, one of which is the amazing seven-kilometer underground river located at St. Paul Subterranean Park at Bgy. Cabayugan, Puerto Princesa City.
The local cottage industry consists largely of shell craft, woodcraft, brassware and metallic craft, needlecraft, food preservation, mat weaving and basket making.
Manufacturing establishments found in the province are small industries like bakeries, lumber mills and shops that turn out hollow blocks, charcoal, rattan, shell craft, salt, vinegar, furniture, kasoy, wine, etc.
Its service establishments range from services on communication, recreation, legal, medical, tailoring and dress shops, beauty parlors, barbershops, repair shops, gasoline service stations, restaurants, and hotels.
Labor force comprises 61.05 % ages from 15 years and above. The remaining is employed either in service (23.47 %) or in industry (6.57%).
STATUS OF ELECTRIFICATION
As of December 2023, PALECO energized 282 barangays out of 371 barangays within its franchise area. It has 210,080 house connections or 74.88 percent of the potential house connection of 280,557 and has 144,718 members. This is continuously increasing because of the ongoing line extensions of the Cooperative funded by National Government, Local Government Units, PALECO itself, and private entities/individuals.
FRANCHISE MAP
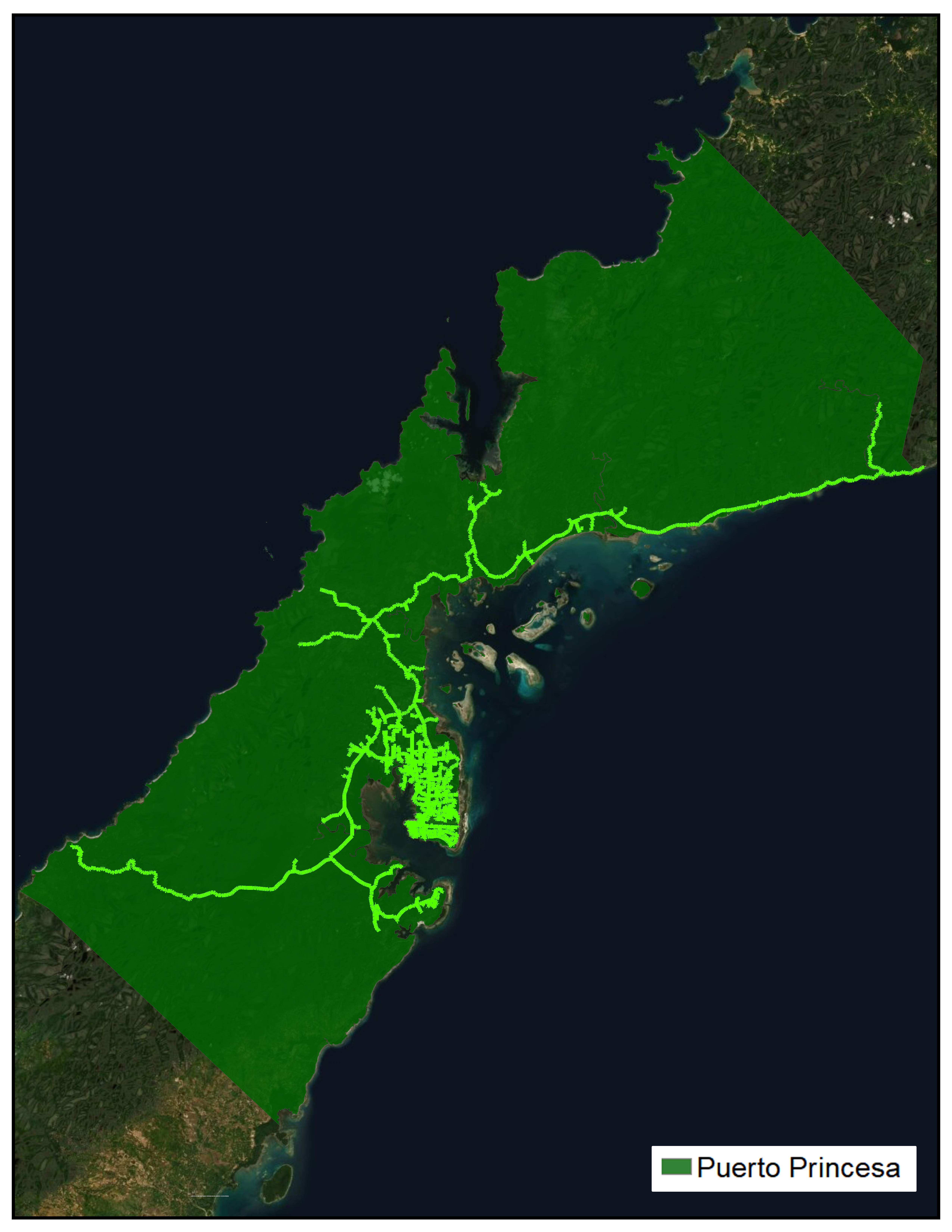
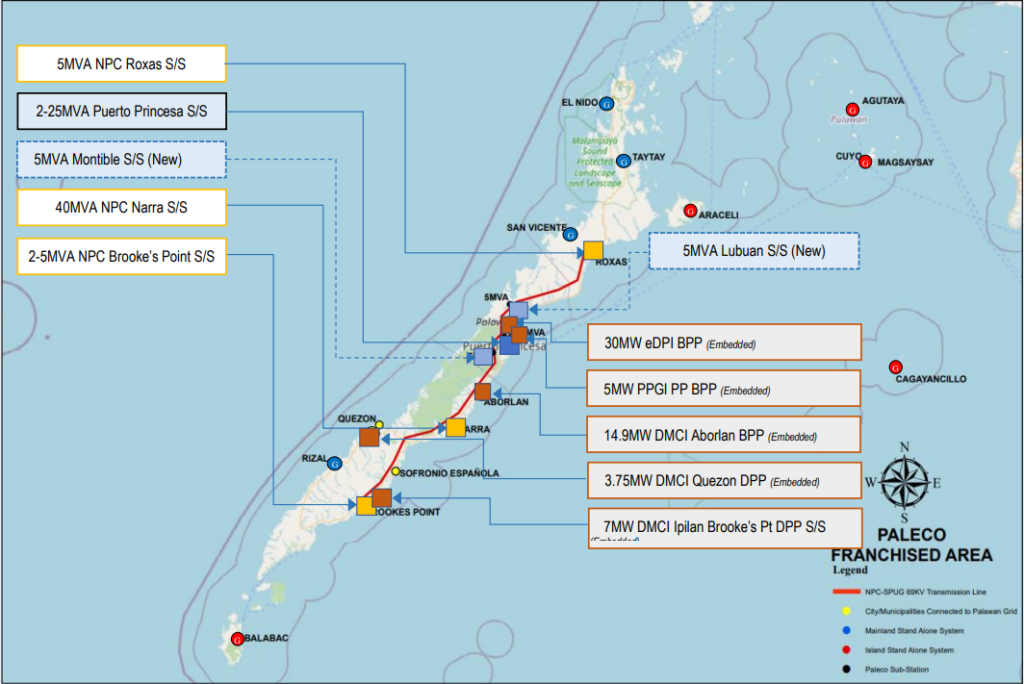
The figure show the system maps for PALECO’s distribution system. There are four (4) systems interconnected to the Palawan Grid and nine (9) are independent or standalone systems.
As of August 2018, sixty eight percent (68%) of the total energy requirement of PALECO’s franchise area is from PPC distribution system.
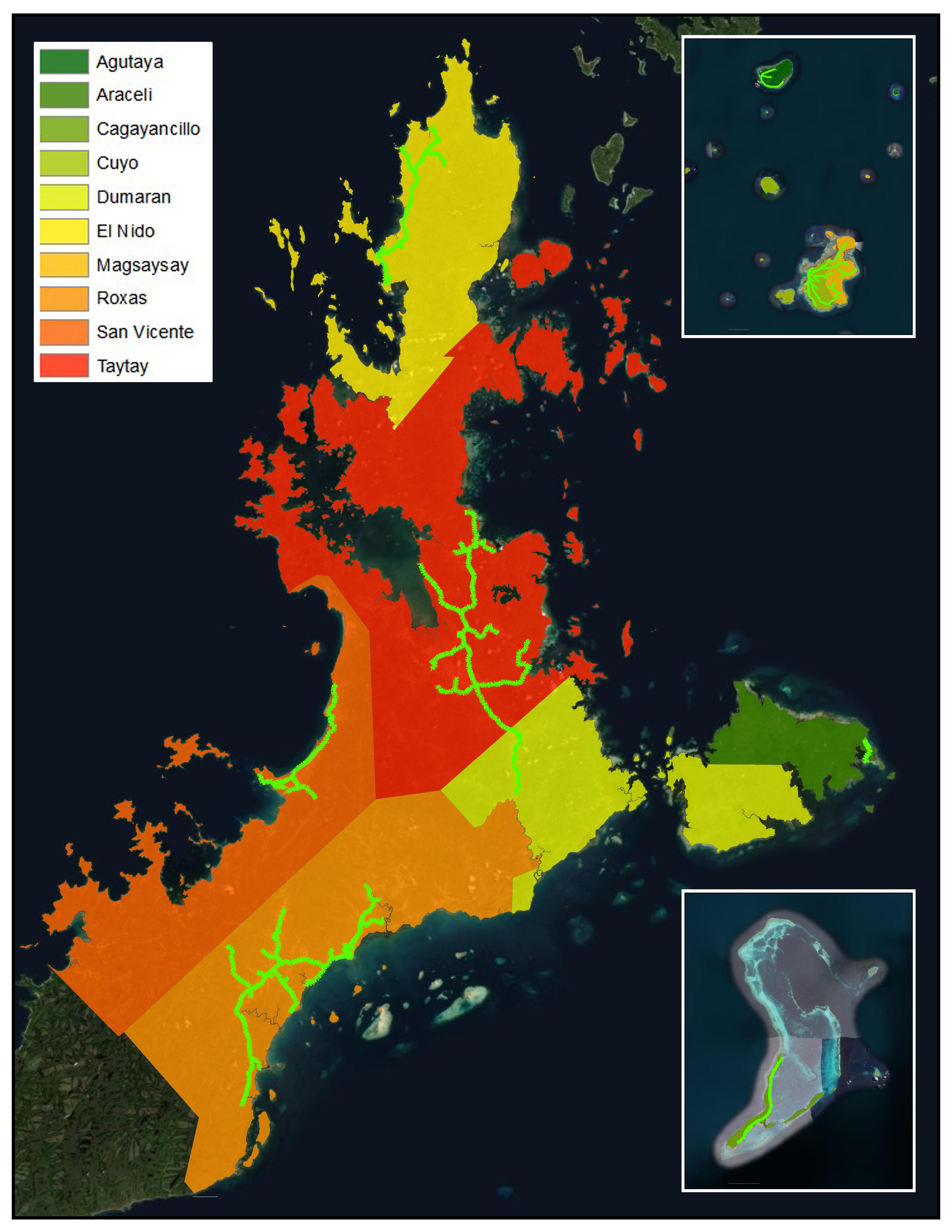
MAINLAND AREAS
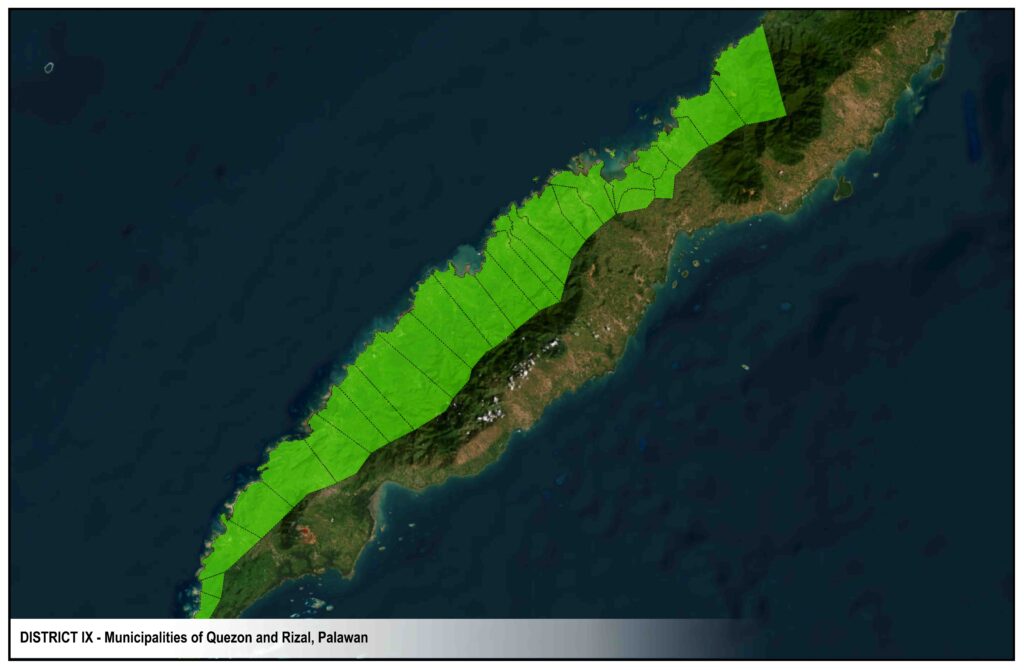
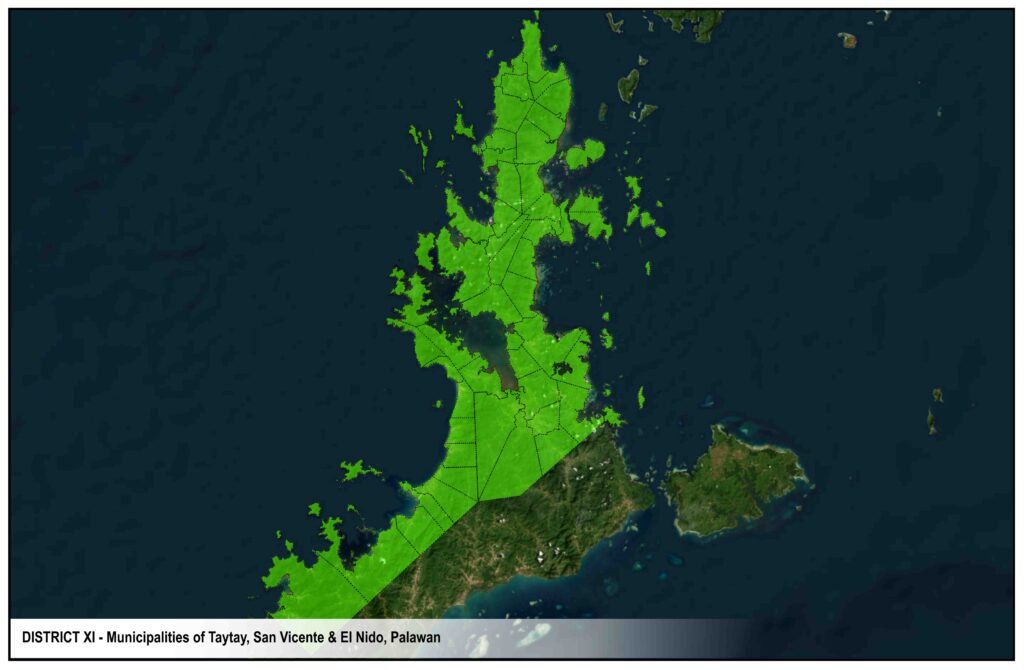
Roxas
San Vicente
Taytay
El Nido
Dumaran
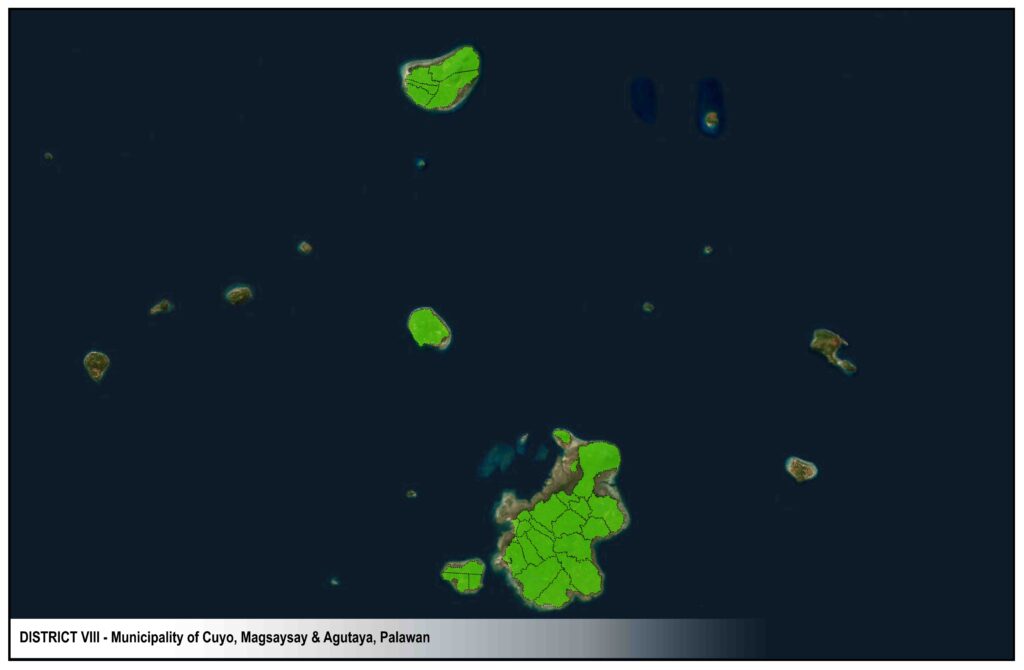
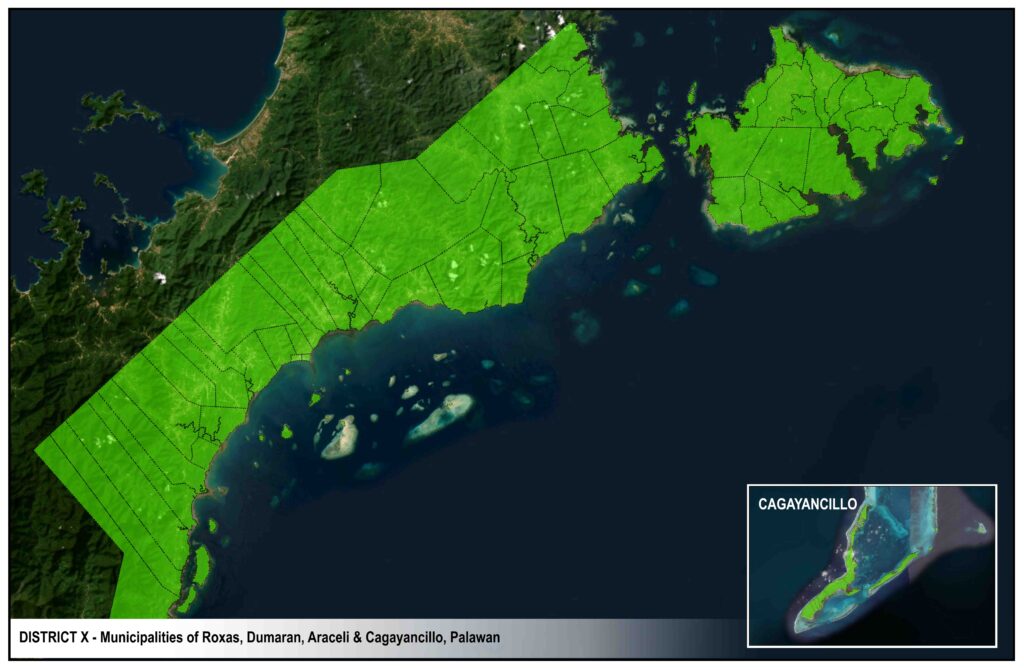
ISLAND AREAS
Dumaran Island
Araceli
Cuyo
Magsaysay
Agutaya
Cagayancillo
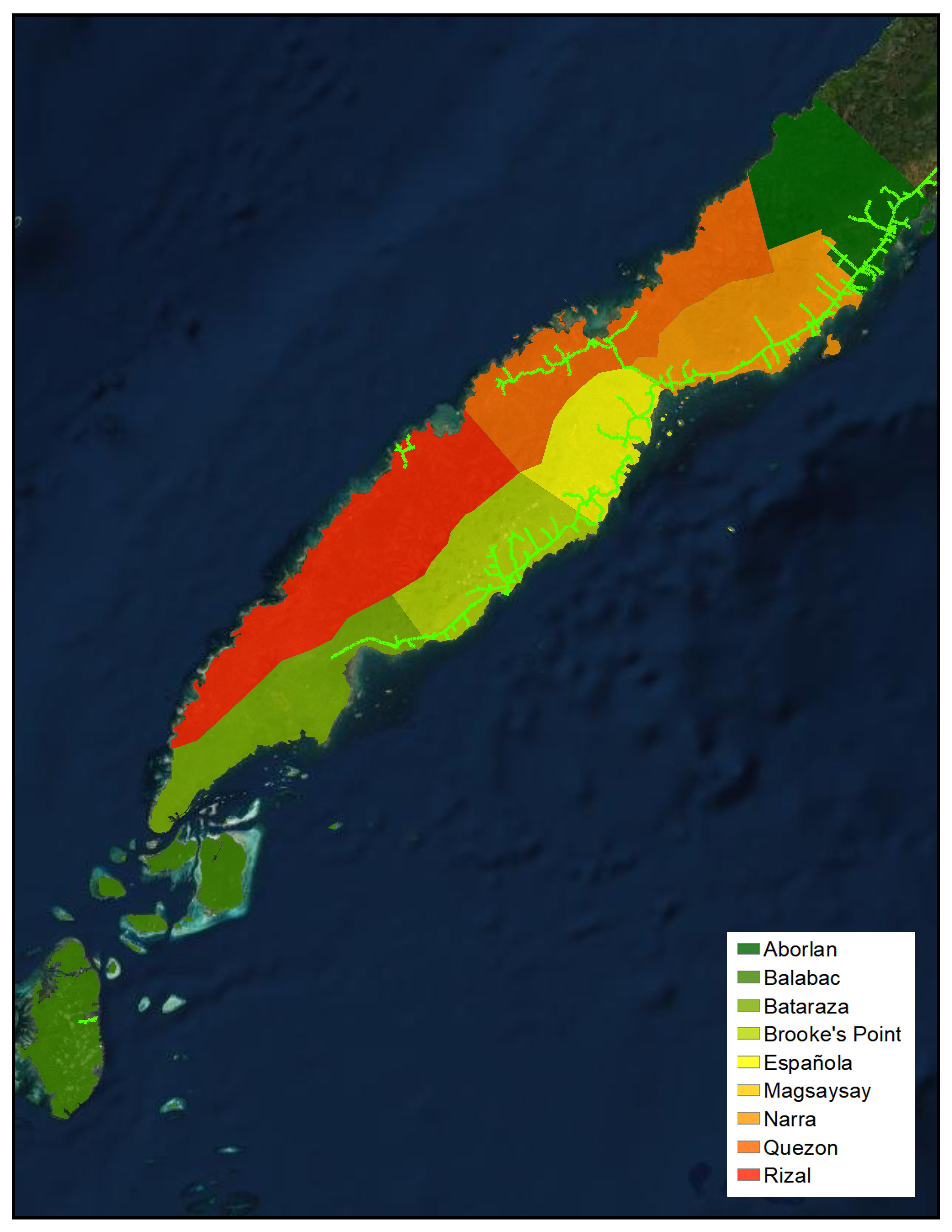
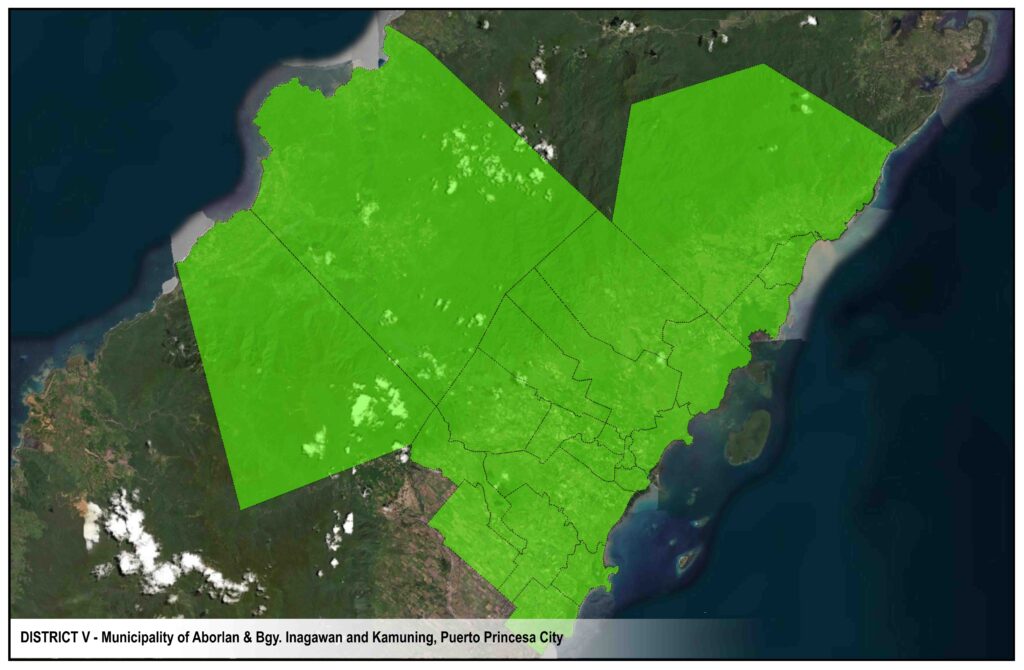
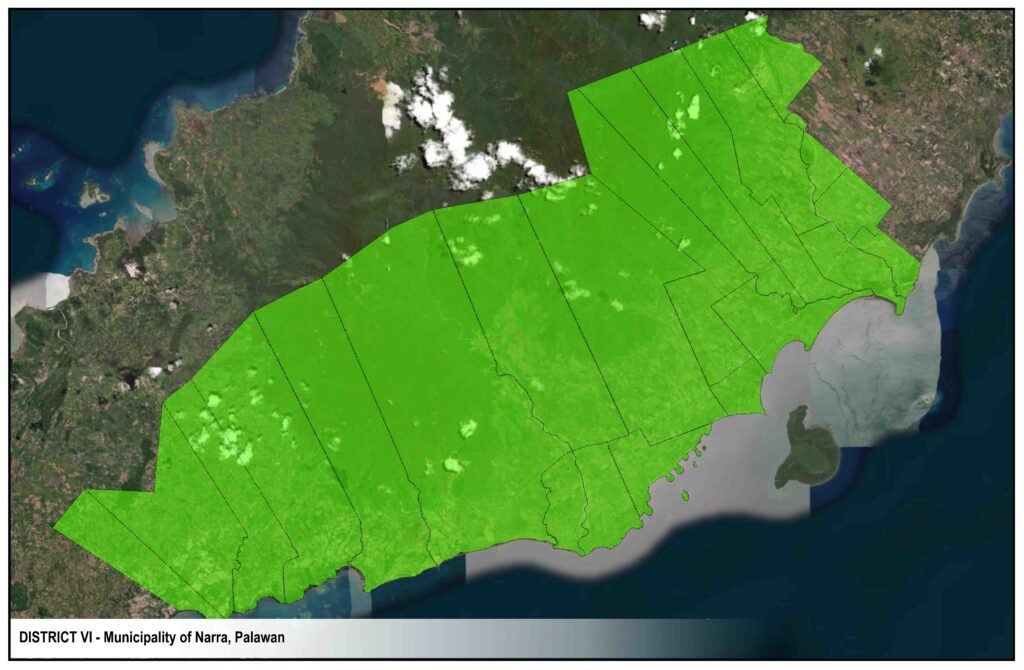
Narra distribution system serves Barangays Inagawan and Kamuning of Puerto Princesa City, the Municipalities of Aborlan, Narra and Quezon and Barangays Abo-abo, Panitian and Isumbo of Municipality of Sofronio Espanola.
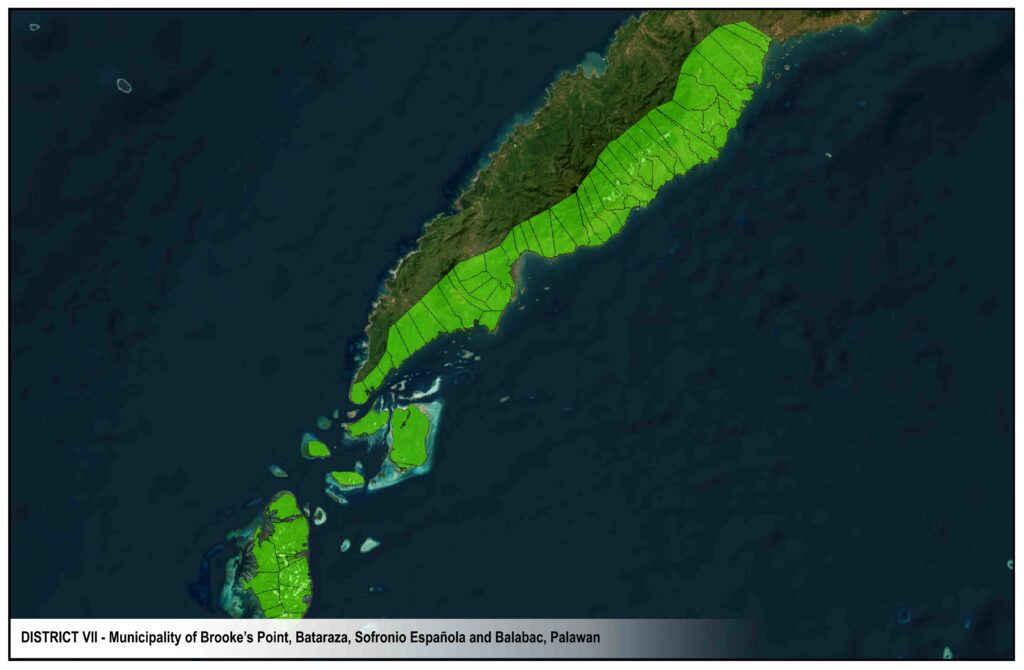
Brooke’s Point distribution system serves the Municipalities of Brooke’s Point and Bataraza and Barangays Pulot, Iraray, Punang and Labog of Municipality of Sofronio Espanola.
DISTRICTS
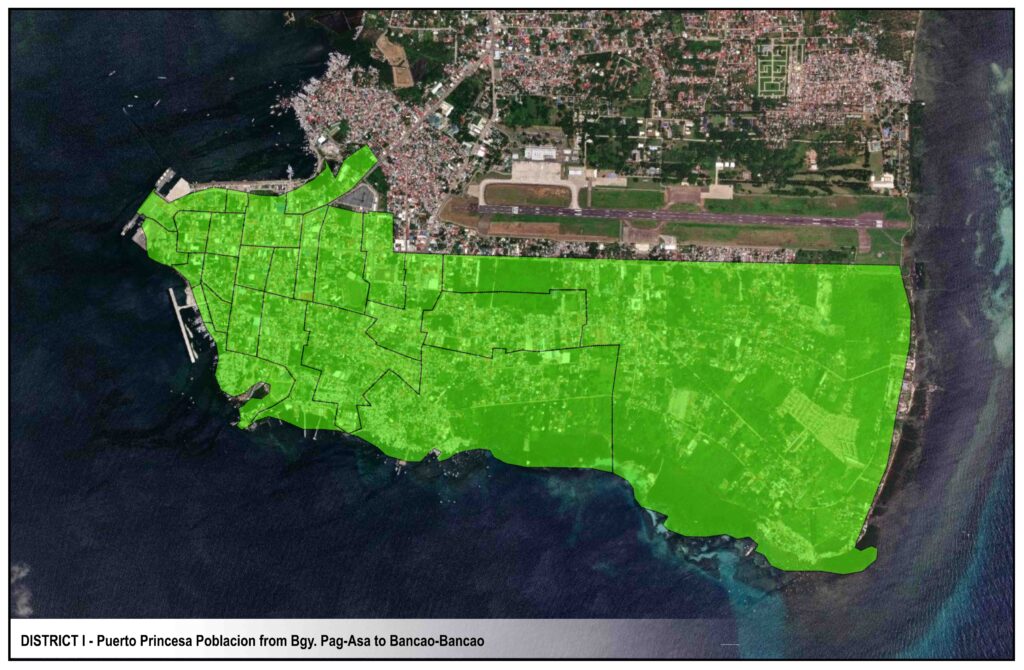
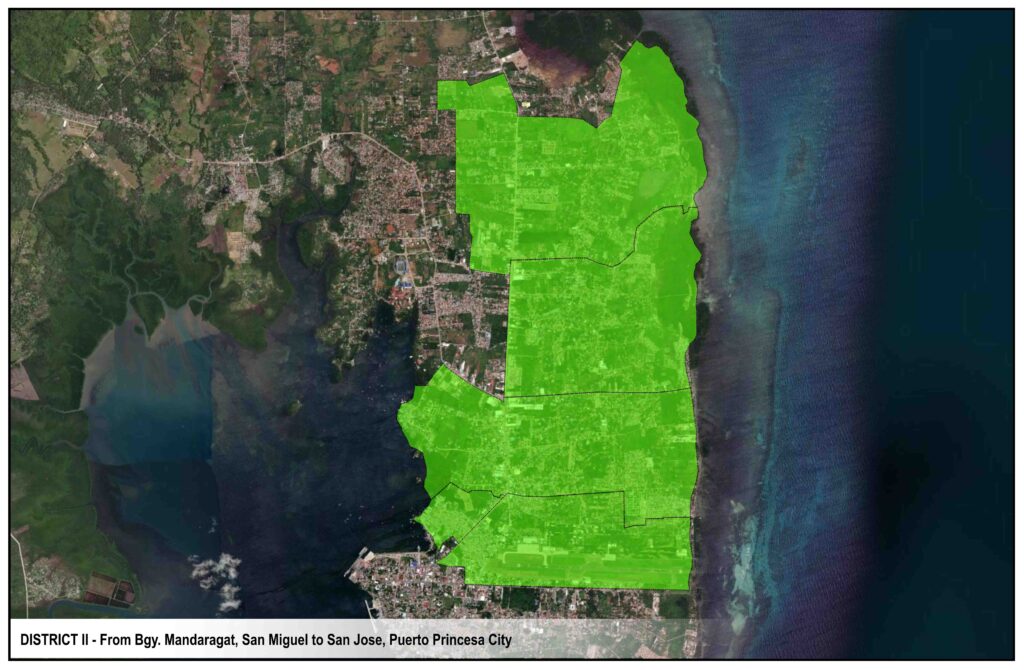
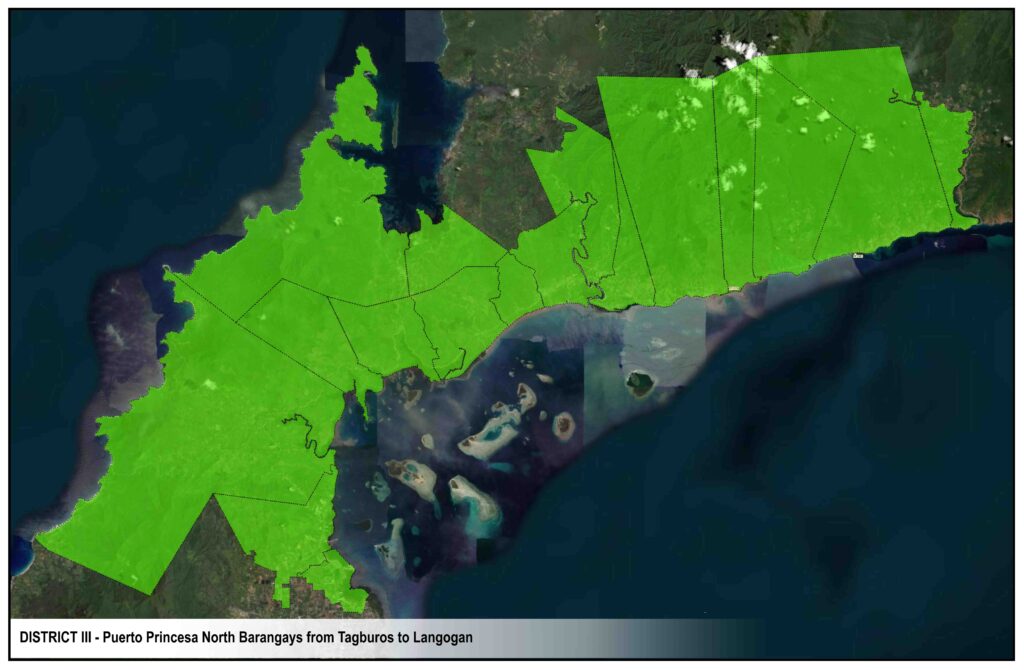
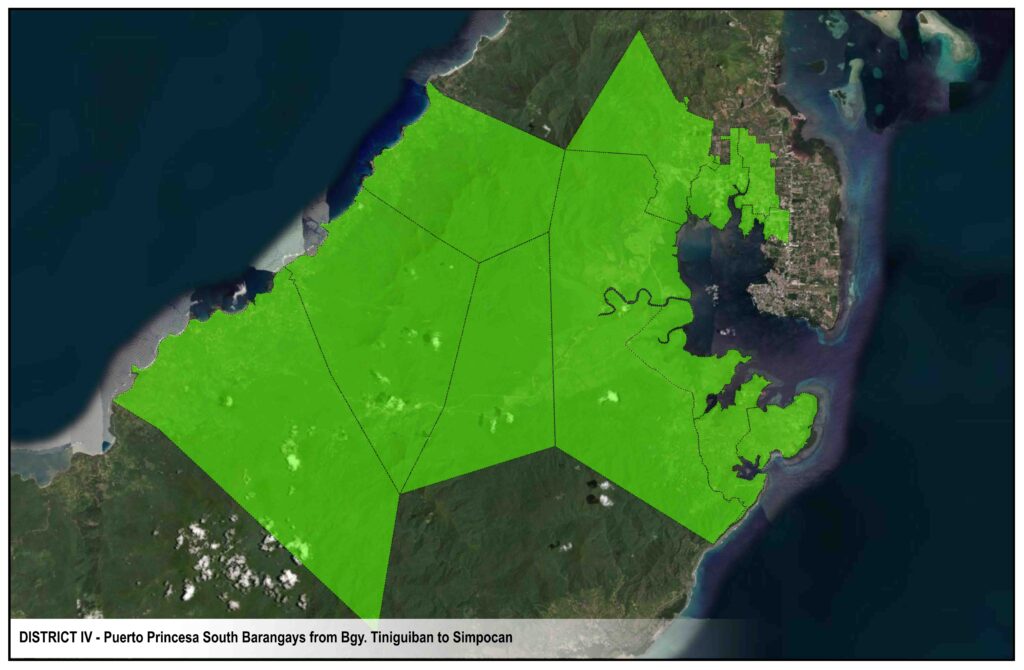
CIRCUITS & RECLOSERS
Portion of Tiniguiban, BIGAA, Asturias Hotel, TAID, UHOA, Kaakbayan, PSU Road., portion of Bgy. San Pedro – Nadayo Road, Abanico Road, Taylor Road, Castro Road, Socrates Road, Malvar St., New Buncag, Old Buncag, Roxas St., Baywalk, Quezon St., Sea Plane Base I & II, Bgy. Matiyaga, Bgy. Bagong Pag-Asa, Port/Pier Area, Concepcion, Quito, Bgy. Liwanag, Taft St., Valencia St., Burgos St., B. Mendoza, Reynoso St., Coop Hospital, Abad Santos, Mabini St., Petron Depot, Manalo St., Fernandez St., Recaido Subd., Liberty Road., Abad Santos Extn. and Altas Sagami.
NADAYAO RECLOSER
Portion of Tiniguiban (UHOA, Kaakbayan, PSU Rdoad), BIGAA, Asturias Hotel, TAID, portion of Bgy. San Pedro – Nadayao Road, Abanico Road, Taylor Road, Castro Road, Pined Road and Socrates Road.
PILTEL RECLOSER
Portion of Roxas, Taft St., Concepcion St., B. Mendoza, Abad Santos St., Reynoso St., Coop Hospital, Mabini St., Petron Depot, Burgos St., Valencia St., Manalo St., Fernandez St., Recaido Subd., Liberty St., Bonas, Abad Santos Extn., Altas Sagami.
MANALO RECLOSER
Burgos St., Valencia St., Manalo, Manalo Extn., Fernandez St., Fernandez Extn., Recaido Subd., Bona, Liberty Rd., Abad Santos Extn. and Altas Sagami.
Portion of Bgy. San Pedro, Delos Reyes Rd. II, City Coliseum, Baltan St., P. Vicente Sr. St., Dacanay Road, Portion of Lacao St., Carandang St., Portion of H. Mendoza, portion of Rizal Ave., portion of Bgy. San Miguel Runway, Junction I, Capitol Compound, Provincial Legislative Building, Lagan Road, Bgy. Bancao-Bancao, Casa Linda, Dagomboy Village, Rengel Road, Airport Compound, ATO/PAGASA Compound, Abrea St., Villarosa Road, portion of Circulation Road, Abueg Sr. Road I, Abueg Sr. Road II, Jacana Road, Gabinete Road, Camella Homes, portion of Manalo at Manalo Extn., Paalan Subd., Princesa Garden, Gacott Road, Pardeco Road, Garcellano Subd., Macawili Rd., Palay Road, PEO Compound, Canigaran and VRC Compound.
CHARIOT RECLOSER
Dagomboy Village, Bgy. Bancao-Bancao, Casa Linda I, Rengel Road, Airport Compound, ATO/PAGASA Compound, Abrea St., Villarosa Road, portion of Circulation Road, Abueg Sr. Road I, Abueg Sr. Road II, Jacana Road, Gabinete Road, Camella Homes, portion of Manalo and Manalo Extn., Paalan Subd., Palawan Garden, Gacott Road, Pardeco Road, Garcellano Subd., Macawili Road, Palay Road, PEO Compound, Canigaran and VRC Compound.
Portion of Bgy. San Manuel, Villa Mervelyn, Mendoza Ville, Typoco, Sir John Subd., Bgy. San Jose – Princeville, NHA Ville, Alta Homes, bgy. Tagburos, Bgy. Sta. Lourdes, Bgy. Bacungan, Bgy. Sta. Cruz, Bgy. Salvacion, Bgy. Bahile, Bgy. Macarascas, Bgy. Manalo, Bgy. Maryugon, Bgy. Lucbuan, Bgy. Maoyon, Bgy. Babuyan, Bgy. San Rafael, Bgy. Tanabag, Bgy. Concepcion, Bgy. Binduyan and Bgy. Langogan.
MENDOZA RECLOSER
Portion of Bgy. San Jose, Bgy. Tagburos, portion of Bgy. Sta. Lourdes, Honda Bay, Bgy. Bacungan, Bgy. Sta. Cruz, Bgy. Salvacion, Bgy. Bahile, Bgy. Macarascas, Bgy. Manalo, Bgy. Maryugon, Bgy. Lucbuan, Bgy. Maoyon, Bgy. Babuyan, Bgy. San Rafael, Bgy. Tanabag, Bgy. Concepcion, Bgy. Binduyan and Bgy. Langogan.
MAGARWAK RECLOSER
Portion of Bgy. Bacungan near Sitio San Carlos, Bgy. Sta. Cruz, Bgy. Salvacion, Bgy. Bahile, Bgy. Macarascas, Bgy. Manalo, Bgy. Maruyugon, Bgy. Lucbuan, Bgy. Maoyon, Bgy. Babuyan, Bgy. San Rafael, Bgy. Tanabag, Bgy. Concepcion, Bgy. Binduyan and Bgy. Langogan.
Portion of Bgy. San Manuel Solid Road, Kalayaan Subd., DJD Subd., Purok Gumamela, Moreno Ville, BM Road, Libis Road, Peneyra Road, Delos Reyes Road I, Hagedorn Road., Wescom Road, AA Plaza, Kalikasan Homes, Ellen View Subd., Western Homes, Naval Road, Hartman Subd., Cunanan Subd., Portion of Bgy. San Miguel – MP Road, San Juan Road and Tankiao HOA.
SOLID RECLOSER
Portion of Bgy. San Manuel- Solid Road, Kalayaan Subd., DJD Subd., Pk. Gumamela, Moreno Ville, BM Road, Libis Road, Peneyra Road, Delos Reyes Road I, Hagedorn Road, Wescom Road, AA Plaza, Kalikasan Home, Ellen View Subd., Western Homes, Naval Road, Hartman Subd., Cunanan Subd., Portion of Bgy. San Miguel – MP Road, San Juan Road and Tankiao HOA.
CABIGUEN RECLOSER
Portion of Wescom Road, Kalikasan Homes, Ellen View Subd., Western Homes, Naval Road, Hartman Subd., Cunanan Subd., Portion of Bgy. San Miguel – MP Road, San Juan Road and Tankiao HOA.
Portion of Bgy. Tiniguiban, Bgy. Sta. Monica, Bgy. Irawan, Bgy. Iwahig, Bgy. Montible, Bgy. Sta. Lucia, Bgy. Luzviminda and Bgy. Mangingisda.
STA. MONICA RECLOSER
Mitra Road, Bgy. Sta. Monica, Bgy. Sicsican, Bgy. Irawan, Bgy. Iwahig, Bgy. Montible, Bgy. Sta. Lucia, Bgy. Luzviminda and Bgy. Mangingisda.
IRAWAN RECLOSER
Portion of Irawan (PPC Water District) PIADP, Bgy. Iwahig, Bgy. Montible, Bgy. Sta. Lucia, Bgy. Luzviminda and Bgy. Mangingisda.
EXISTING POWER PROVIDERS,
TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION LINES
PALECO operates under difficult circumstances due to its archipelagic categorized as missionary area for electrification. The National Power Corporation-Small Power Utility Group (NPC-SPUG) and three Independent Power Producers (IPPs) namely, Delta P Incorporated (Delta P), Palawan Power Generation Incorporated (PPGI) and DMCI Power Corporation supply the energy requirements of PALECO. Presently NPC-SPUG has a transmission line from Puerto Princesa City to the municipality of Brookes Point. Only Puerto Princesa and the municipalities of Aborlan, Narra, Quezon, Espanola, Brookes Point and Bataraza are interconnected in the grid. The rest of the municipalities including those in the islands have its own individual distribution systems with small stand-alone generating plants owned by NPC-SPUG.
SMALL POWER UTILITIES GROUP
Palawan is under National Power Corporation (NPC) – SPUG, which is mandated by law to undertake the missionary electrification of areas not connected to the main transmission grid. Thus, PALECO consumers benefit from the subsidies prescribed for SPUG areas.
In the so-called Palawan Grid, NPC-SPUG maintains the 69 kV and 13.8 kV transmission line while PALECO acts as the System Operator. In contrast, for the ten (10) separate distribution systems of PALECO, NPC-SPUG operates and maintains the power plants that supply the power requirement of each system.



